What are Vectors and Embeddings?
Large Language Models (LLMs) can't process all the information at once due to limited context windows, which can lead to hallucinations. To prevent this, we give them access to only the relevant data when needed. This is where vectors and embeddings come into play.
Vectors are a way to represent data using numbers used in machine learning, a powerful way to represent and manipulate data. In the context of RAG, we take the data and generate embeddings (vectors) for each piece of data. The core idea of embeddings is that semantically closer data points are closer in the vector space.
A typical vector embedding for a piece of data might look like this:
[-0.2, 0.5, 0.1, -0.3, 0.7, 0.2, -0.1, 0.4, 0.3, ...]
The length of a vector array is called its dimension. Higher dimensions allow the vector to store more information. Think of each number in the vector as representing a different feature of the data. For example, to describe a fruit, features like color, taste, and shape can each be represented as a number in the vector.
The choice and representation of these features form the art of creating embeddings. Effective embeddings capture the essence of the data compactly, ensuring that semantically similar data points have similar embeddings.
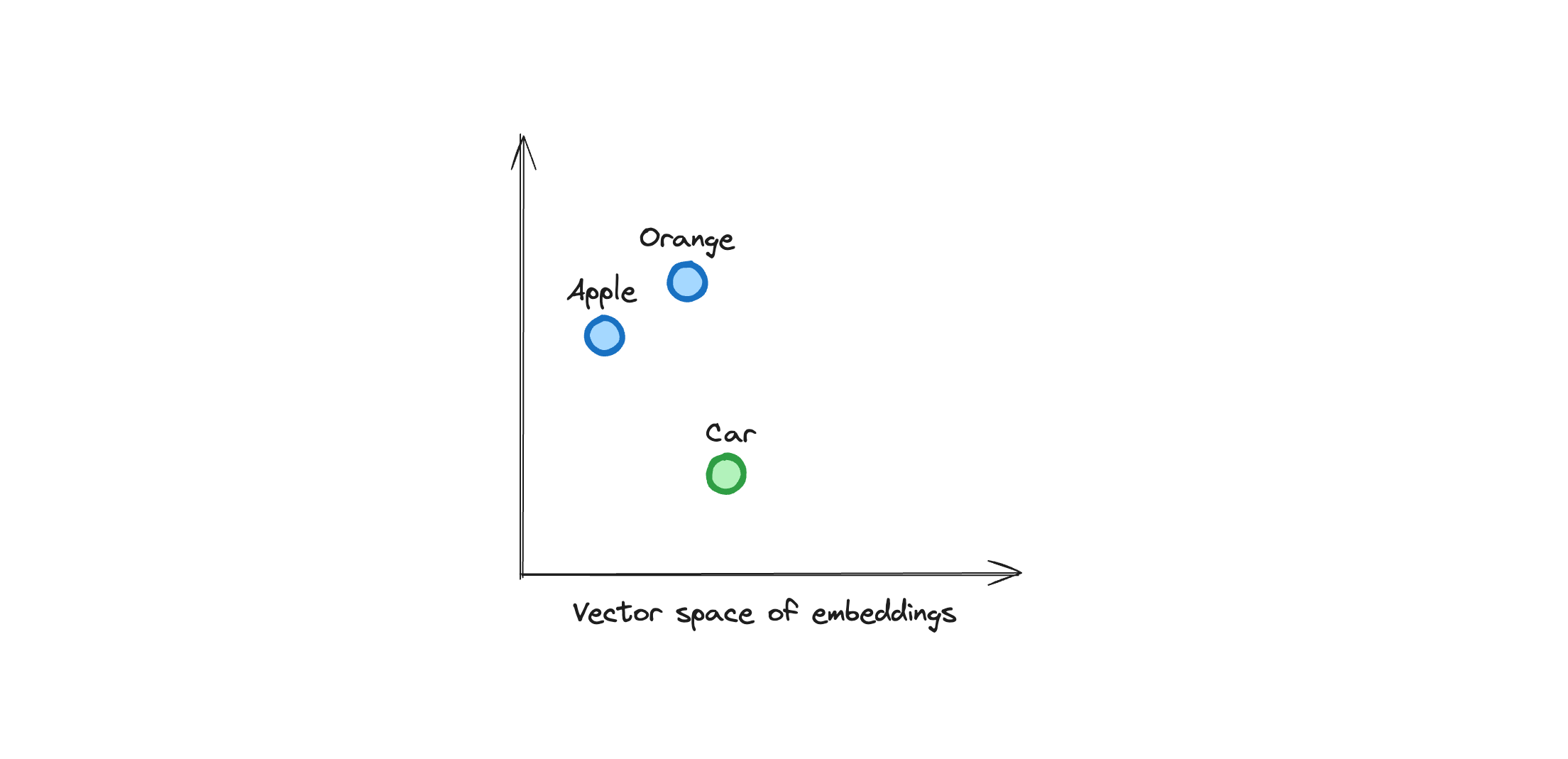
For instance, "apple" and "orange" are closer in the vector space than "apple" and "car" because they are semantically similar. They will appear closer in the vector space. Look at the image below to visualize this concept.
Data can be of any sort, such as text, images, and audio. Langbase embeds this data into vectors and stores them in a vector database. The goal is to store relevant information in the vector database and provide LLMs with a way to access it, known as retrieval.
Here’s a diagrammatic representation of Langbase’s memory (vector) store:

Here are the different types of vector embeddings:
- Word embeddings: Represent individual words in a continuous space, often used in tasks like sentiment analysis, language translation, and word similarity.
- Sentence embeddings: Capture the meaning of entire sentences, useful for sentiment analysis, text categorization, and information retrieval.
- Document embeddings: Represent entire documents, used in document similarity, clustering, and recommendation systems.
- User profile vectors: Represent a user's preferences or actions, applied in customer segmentation and personalized recommendations.
- Image vectors: Represent visual items like pictures or video frames, used in object recognition and image search.
- Product vectors: Represent products, used in product searches, classification, and recommendation systems.
Vector embeddings power many essential applications, including:
-
Personalized Recommendations: Used by platforms like Netflix and Amazon to match user preferences with items by turning both into vectors, making recommendations more accurate and customized.
-
Enhanced Search: Search engines leverage embeddings to grasp meaning beyond exact matches, retrieving results based on context and relevance.
-
Chatbots & Q&A Systems: Embeddings enable chatbots to understand and generate meaningful responses. Models like GPT-4o-mini and tools like DALL-E use embeddings to respond contextually in human-like conversations.
-
Anomaly & Fraud Detection: Embeddings help spot unusual patterns or outliers by measuring vector distances, supporting fraud and anomaly detection.
-
Data Preprocessing for ML: Embeddings convert raw data into vectors, simplifying the data for machine learning models.
-
One-Shot & Zero-Shot Learning: Embeddings allow models to predict new categories with minimal data, using semantic insights for broader generalization.
-
Similarity & Clustering: Vector embeddings make it easy to calculate similarities and group related items, supporting high-dimensional comparisons and clustering.
In this guide, we covered vectors and embeddings, showing how they help AI find and use data efficiently. Langbase’s Memory Store turns different data types into vectors, allowing LLMs to access only relevant information. This improves accuracy and reduces errors, making embeddings crucial for AI tasks like recommendations, search, and chatbots.
For more details read here.